Cable Removal and VBR Replacement Delivered Offshore Without Shutdown
Client / Site: NKT / Offshore Wind Farm – Renal Wind Farm
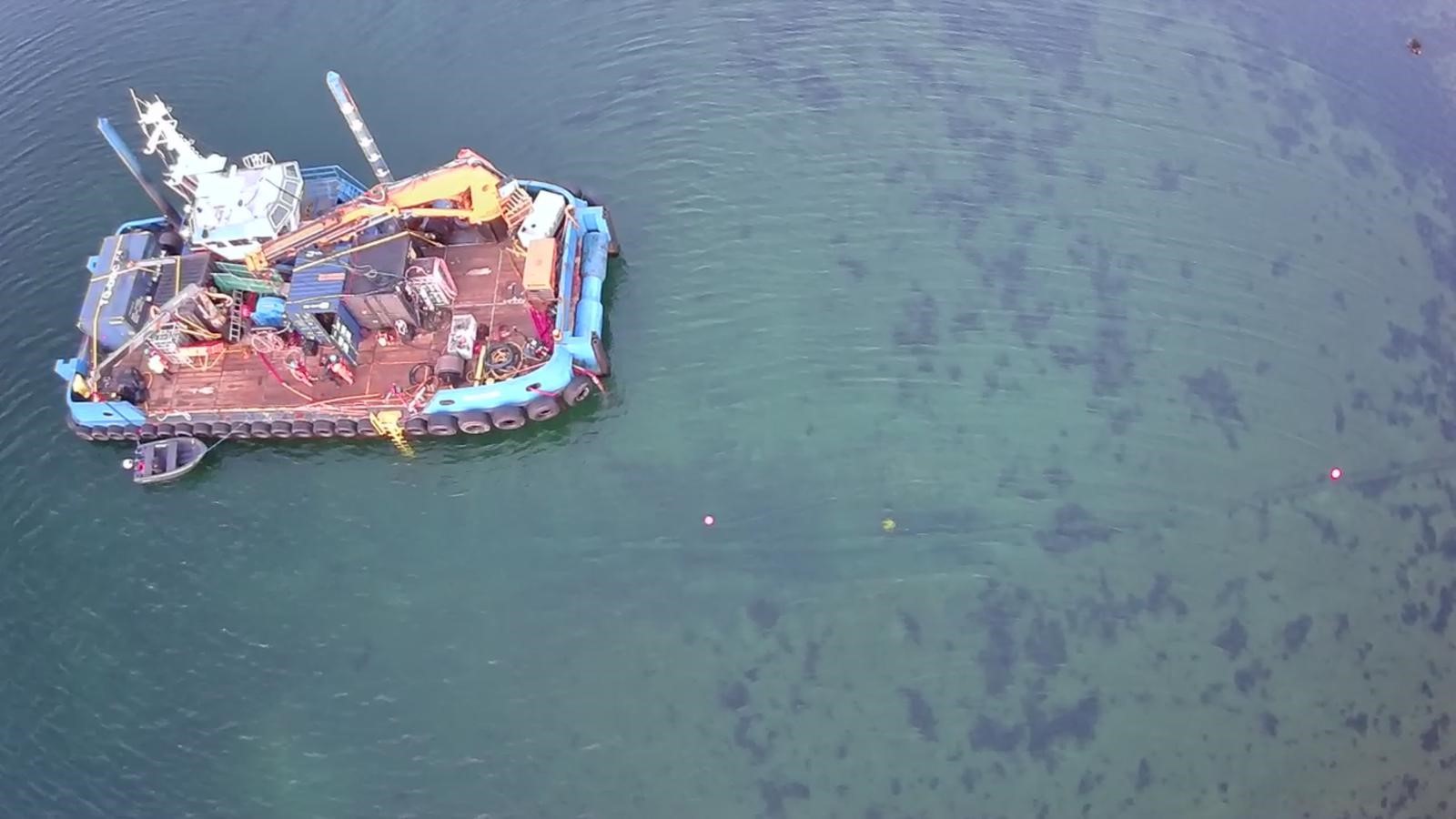

NKT required the safe cable removal of a retired subsea export line and the replacement of a compromised Vented Bellmouth Receptacle (VBR) — a funnel-shaped entry point that protects and guides power cables as they enter a wind turbine foundation.
This was not a straightforward task, as our team faced multiple challenges:
- Live turbine operations – We needed to complete all work without shutting down the turbine, requiring strict high-voltage (HV) safety measures and close coordination with the Transmission System Operator (TSO).
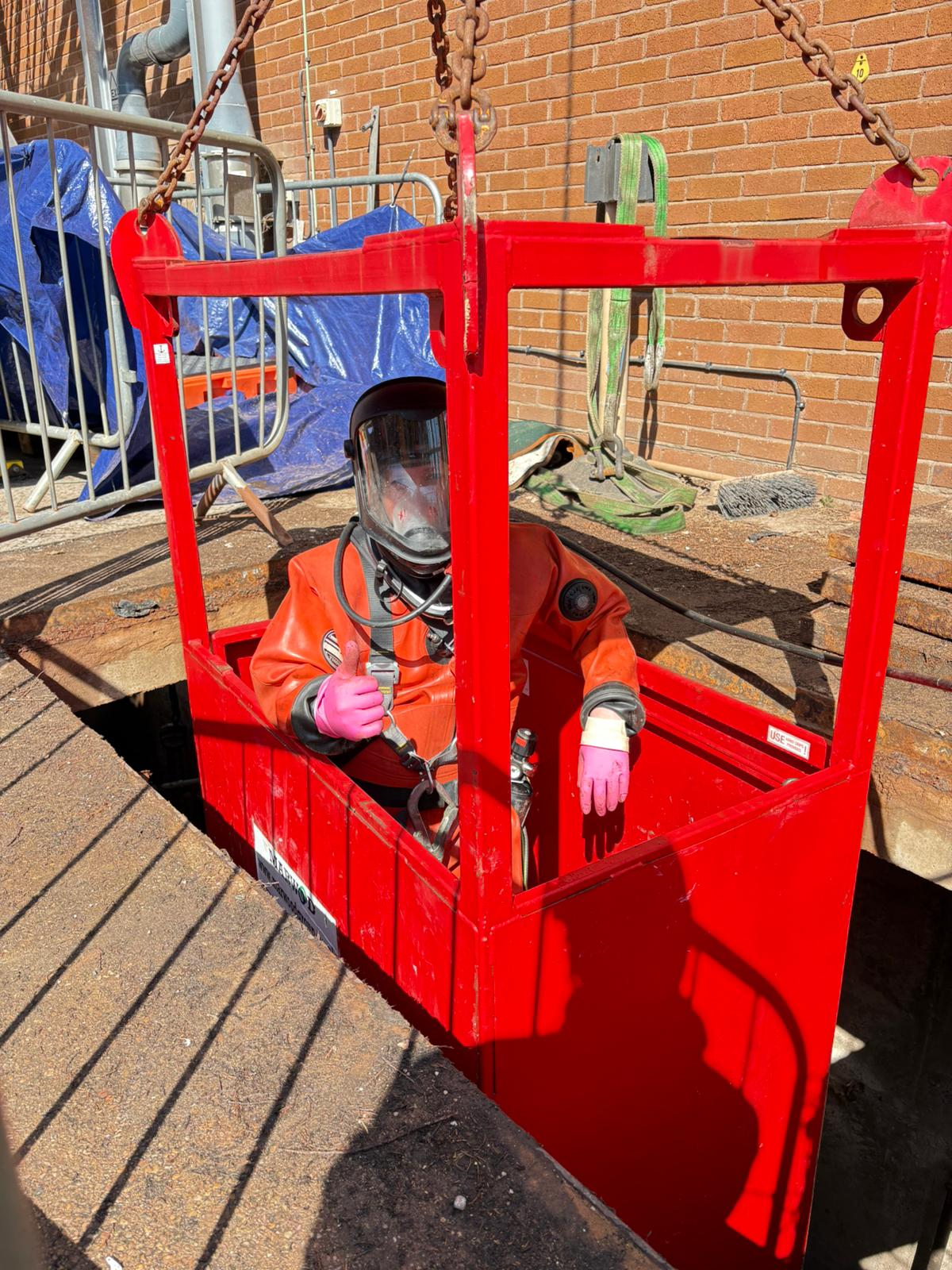
- Restricted subsea access – Marine growth and corrosion obstructed the J-tube interface (the protective conduit for the cable), which meant poor visibility and a difficult working environment to use tools.
- Dual objectives – Our specialist dive team had to deliver both the subsea cable removal and VBR replacement in a single offshore campaign window.
Our Response
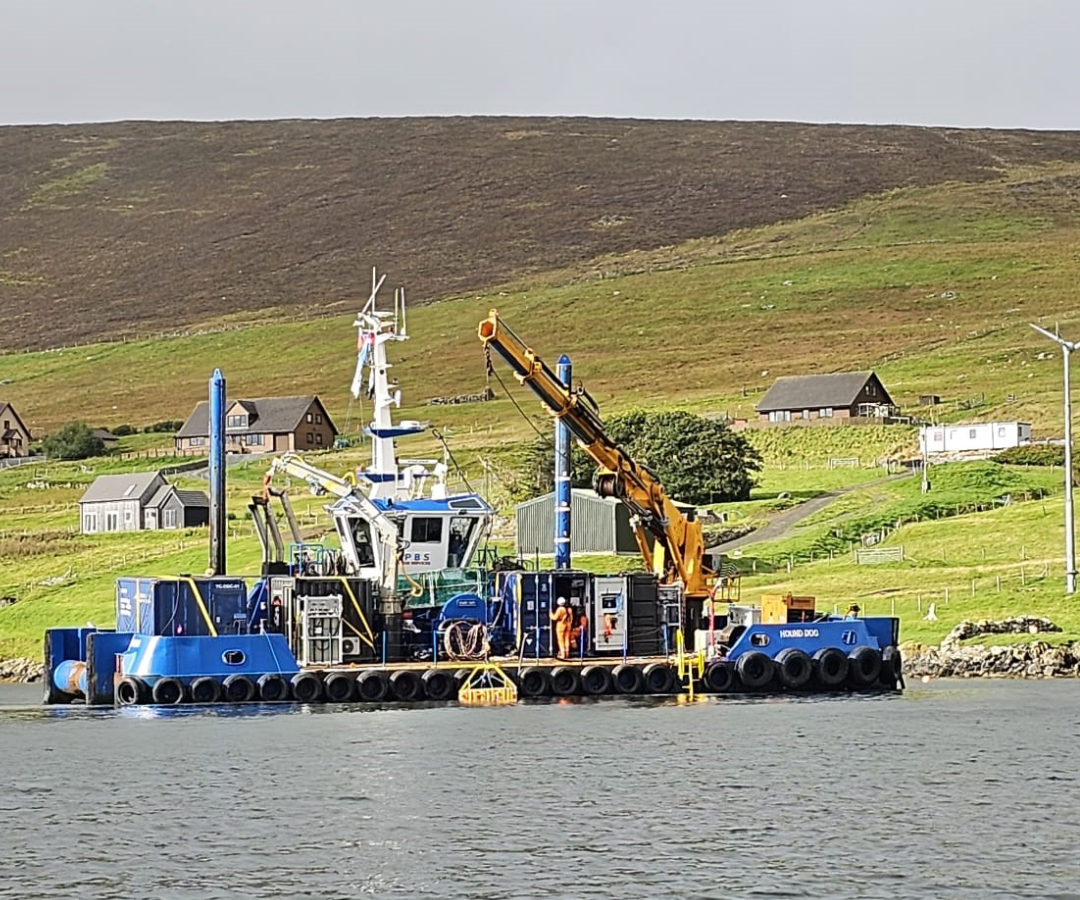
Dagger Diving mobilised an offshore-qualified air diving team supported by a vessel-based dive control system. From there, we began our operations, which involved working under a comprehensive Permit to Work system. Isolations were confirmed by NKT, the TSO, and the foundation operator.
Export Cable Removal:
- Divers detached the retired subsea cable from internal supports and J-tube brackets.
- Using hydraulic tensioning systems, the cable was carefully extracted and recovered to deck for safe disposal.
- Cold-cutting tools (which avoid heat and sparks) were used to eliminate risks to surrounding components during cable removal.
VBR Replacement:
- The old VBR was safely disconnected and removed using pre-installed guide rigging.
- A new VBR was lowered into position, aligned with its mechanical interface, and secured using diver-deployed torque tools.
- Final alignment and fit were verified through tactile checks and high-definition helmet camera feeds.
- Integrity tests confirmed the new VBR was unobstructed, secure, and ready for future re-cabling operations.
All subsea assets were inspected, and the condition of marine growth was logged to support future maintenance planning.
The Outcome
Mission Accomplished: The entire project was completed efficiently and without incident, ensuring cable removal and VBR replacement were delivered within the operational window.
Results achieved:
- Retired export cable fully removed
- New VBR installed with 100% mechanical integrity
- No interruption to turbine output during operations
- Zero lost-time incidents or electrical safety breaches
- Comprehensive subsea condition reporting provided to NKT
The success of the project meant the infrastructure was fully prepared for upcoming grid upgrades — all while maintaining live turbine operation.
Compliance: Delivered in line with IMCA D018, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 45001, and client HV interface procedures.
Technical Note: What is a VBR and Why Does it Matter?
A Vented Bellmouth Receptacle (VBR) is a subsea entry point that guides and protects power cables as they are routed into offshore wind turbine foundations. The “vented” design reduces pressure changes and allows trapped air or water to escape during installation. Without a secure VBR, cables risk damage from abrasion, bending, or blockage — making VBR integrity critical for the long-term reliability of offshore power infrastructure.








Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.